
Enhance the understanding of extreme environments to contribute to the Ocean Decade.
The UN Decade of Ocean Science for Sustainable Development, known as the Ocean Decade, represents the largest global initiative focused on ocean science. It addresses ten challenges aimed at transforming the way we generate and apply marine research. This blog briefly discusses how developing new methods to understand, represent, communicate, and engage with extreme marine environments can help address these challenges.
By Valentina Lanci
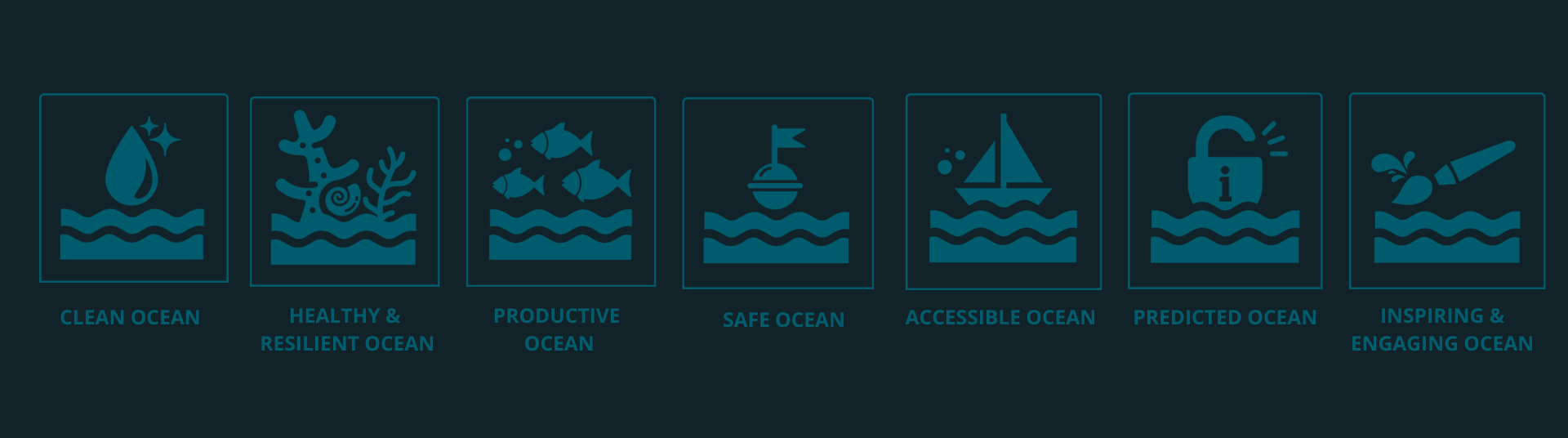
Seven social outcomes and ten key challenges for the Decade.
As we observe the adversities affecting ocean health, particularly in the Arctic and other vulnerable regions, it is crucial to realize the significant impact these changes have on our heritage, cultures, livelihoods, security, and overall well-being.
In this regard, the UN Ocean Decade brings together individuals from diverse fields to forge meaningful scientific solutions for the ocean. Guided by the vision of “the science we need for the ocean we want,” this collaborative effort supports countries in achieving their ocean priorities outlined in the 2030 Agenda, especially Sustainable Development Goal 14, which emphasises the conservation and sustainable management of ocean resources.
The Ocean We Want is effectively outlined in the 7 Ocean Decade Outcomes, presenting ten ambitious challenges that are essential for achieving these transformative outcomes.
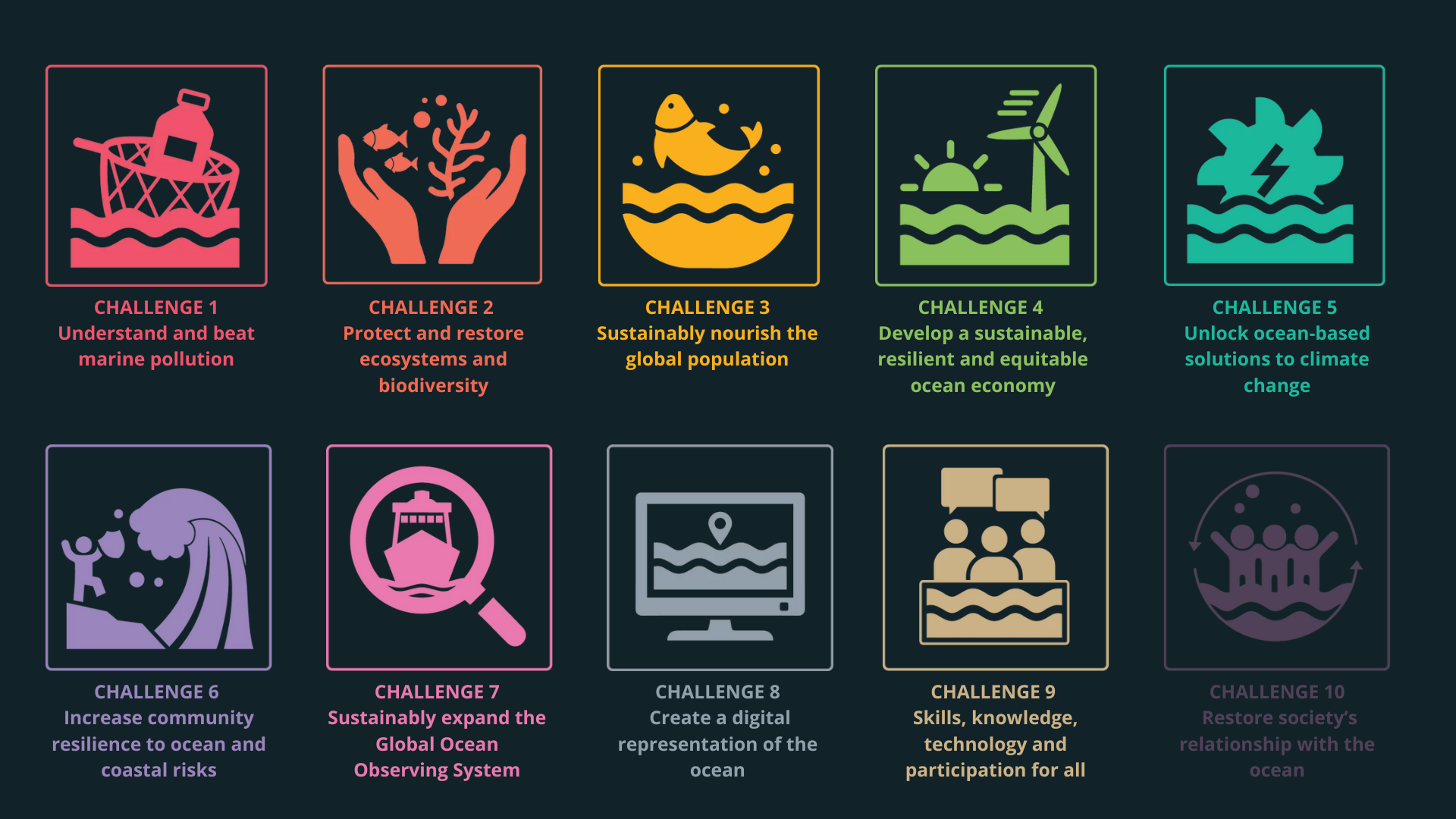
The Ocean Decade Challenges highlight the most urgent and significant priorities that need to be addressed at various levels—global, regional, national, and local - and shape the overarching contributions of the Decade. By focusing on these challenges, partners within the Decade can collaborate effectively, fostering a united effort toward the sustainable management and protection of our oceans.
The ten challenges cover a broad spectrum of goals, including the development of a resilient ocean that safeguards vital ecosystems and supports coastal communities. Additionally, they emphasize the importance of creating an ocean that is accessible to everyone, where data and innovation are distributed equitably, ensuring that all communities can benefit from advancements in ocean science and technology.
The EXTREMES project and its contribution to the Decade.
In order to gain a comprehensive understanding of the ocean, the scientific community must recognize the importance of investigating its extreme environments. These key areas are vital for understanding the complexities that exist within ocean systems.
The ocean presents a range of challenging conditions, such as high-pressure zones in the deep sea, icy temperatures in polar regions, and unique ecosystems surrounding hydrothermal vents. These extreme environments play a crucial role in the overall functioning of ocean systems, significantly influencing marine biodiversity and ocean circulation patterns. By studying these habitats, we can gain important insights into the resilience of life, the impacts of climate change, and the interconnectedness of oceanic processes.
Therefore, to fully appreciate our oceans, we must explore and understand these fascinating and often harsh environments. That's why, in accordance with the priorities established by the Ocean Decade, the project EXTREMES (https://uit.no/project/extremes) aims to bring a significant contribution to one or more of the ten Ocean Decade Challenges, which highlight the most pressing needs in ocean science.
ONE. EXTREMES can contribute to “increase community's resilience to ocean hazards”(Challenge 6)
Community resilience, which can be defined in various ways, includes key elements such as social cohesion and collaboration. In this context, the Extremes project aims to co-create a shared community vision for resilience in relation to natural hazards and climate change, emphasizing a positive narrative. To achieve this goal, the scientists and professionals participating in the project will work closely with local communities in Iceland. Their efforts will include organizing workshops and informational sessions to foster dialogue and collaboration. In addition, they will engage with policymakers and industry stakeholders from partner countries to ensure that diverse perspectives are considered.
Together, they will focus on promoting sustainable practices and implementing responsible resource management strategies in the Arctic region. This collaborative approach aims to balance environmental preservation with the economic needs of the communities involved, ensuring a sustainable future for the region's natural resources.
The project's primary goal is to establish a foundation for a new network that facilitates this engagement by bringing together interested researchers, artists, and stakeholders. This network will focus on interdisciplinary exchanges and activities aimed at exploring innovative ways to understand, represent, communicate, and connect with extreme marine environments.
By engaging youth, artists, municipal officials, and community members in various activities—such as co-creation workshops, art installations, and exhibitions—the project aims to enhance knowledge about weather and climate, the risks from local hazards, and strategies for mitigation. It also encourages the community to reflect on the concept of resilience.
TWO. EXTREMES contribute to “create a digital representation of the ocean”, developing “skill, knowledge and technology for all” (Challenges 8 and 9)
While these extreme environments are highly important and interesting places from ecological, political, and business perspectives, they are often poorly studied, rarely represented, and little present in the imaginations and minds of those not directly engaged with them.
The project's goal is to build capacity and develop effective ways to represent extreme marine environments, fostering responsible and sustainable relationships with these areas. The project aims to create a comprehensive digital representation of the ocean that will serve as a valuable resource for all.
In this context, the EXTREMES experts have designed an online course titled "Extreme Environments." This pioneering educational initiative was developed at UiT, The Arctic University of Norway, in collaboration with other universities and international institutions. The course is designed for undergraduate, graduate, and doctoral students from various fields, including geology, biology, environmental science, and governance. It is also suited for individuals interested in exploring extreme environments. Emphasizing interdisciplinary and research-based active learning, the course provides valuable insights and tools to prepare students for advanced studies or careers in environmental and planetary sciences (To know more: https://uit.no/project/extremes/education ).
This course is offered online through an open platform, employing advanced digital technology to facilitate an immersive educational experience that transcends geographical and logistical limitations. The initiative seeks to enhance participants' skills and knowledge related to marine environments while promoting the utilization of cutting-edge technologies.
A notable component of the course is the virtual cruise which has been developed based on a previous project and specifically implemented by a master's student for this course. This feature serves to enrich the learning experience and provides participants with unique insights into marine ecosystems.
(Virtual Cruise link: https://www.thinglink.com/scene/1871662911974277606)
THREE. EXTREMES aims to “change humanity’s relationship with the ocean” (Challenge 10)
The exploration of extreme environments offers valuable insights into the Earth's interior. By bringing water and fine sediments from depths ranging from several hundred meters to a few kilometres, these environments not only reveal details about the Earth's geological history but also provide information about potential future ecosystems that may develop around these phenomena.
While traditional geological and biological methods provide observations into the complexities of ocean environments, incorporating aesthetic and socio-cultural considerations can lead to a deeper and more nuanced understanding.
By exploring both the scientific aspects and the artistic and cultural dimensions of our interactions with the ocean, the experts participating in this project attempt to achieve a more comprehensive understanding of the ocean’s significance in our lives. This inspiring multidisciplinary approach aims to transform humanity's connection with the ocean, promoting a deeper appreciation for its beauty and vital role in sustaining our ecosystem and well-being.

