
Ph.D. Jayalal Kalathilparambil Jayanthan
The effect ofNovel Marine Foods on the Gut Microbiome and its rolein Atherosclerosis
The gut microbiota is the collection of living microorganisms that includes bacteria, anaerobic fungi, and viruses that live in the digestive tract of animals, i.e. the combination of all genomes (genome: complete set of genes or genetic material) of the microorganisms present in a particular environment. The human gut microbiota has about 100 times as many genes as a human genome. The human gut has the most significant number of microbes, especially bacteria, and the greatest number of species anywhere else in the body. This gut microbiome is environmentally acquired from birth and shaped by the host's lifestyle, mode of birth and diet. It acts as a biological filter in the gut, producing molecules that can be beneficial or harmful, affecting the host's immune system and metabolism.
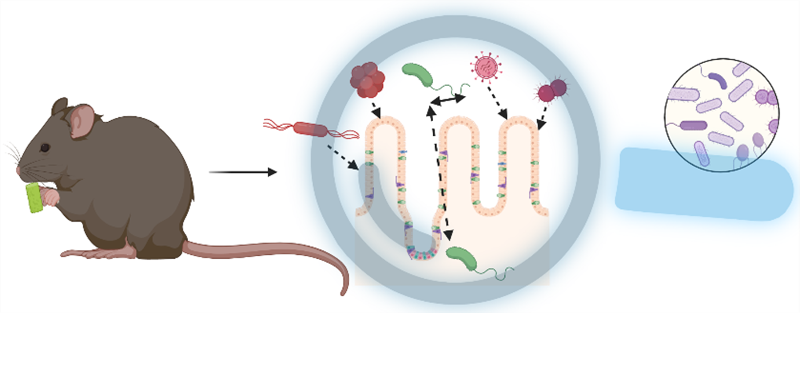
Environmental factors such as the lifestyle of individuals, diet, and medication can determine the composition and function of gut microbiota. Socio-environmental framework studies show that the diet's nutritional value, food abundance changes, and food systems' safety have affected human health and sustainability since 1961. By connecting these socio-ecological framework reports, it was found that the number of cases associated with cardiometabolic diseases is increasing worldwide, and atherosclerosis is one of them. Atherosclerosis is a complex disease involving chronic inflammatory and metabolic pathways modulated by the gut microbiota; this suggests a compelling set of links between diet, gut microbiome, and atherosclerosis. The microbiome can affect atherosclerosis (a disease of the arteries where fat builds up on the inner walls) in three ways: microbial infection, altered cholesterol metabolism, and specific food components and metabolites.
The good news is that human cardiometabolic health benefits have been documented from seafood consumption. The marine-low-trophic-levels-species considered are primary-level organisms that humans have not widely consumed. At the same time, they have been eaten by a secondary-level organism in the marine food chain. Nonetheless, the benefits of novel seafood from lower trophic levels associated with cardiometabolic health, atherosclerosis and gut microbiome are not well studied. Several questions remain to be answered to understand the underlying mechanisms and causal relationships responsible for the development of atherosclerosis, marine-low-trophic-levels-species nutrition, gut microbiome, and gut microbial metabolism. During my PhD, I will use the atherosclerosis mouse model to explore the intestinal tract microbiome using metagenomics/metatranscriptomics after feeding marine-low-trophic-level species to the experimental animals.