Blood biomarkers as early predictors of type 2 diabetes mellitus
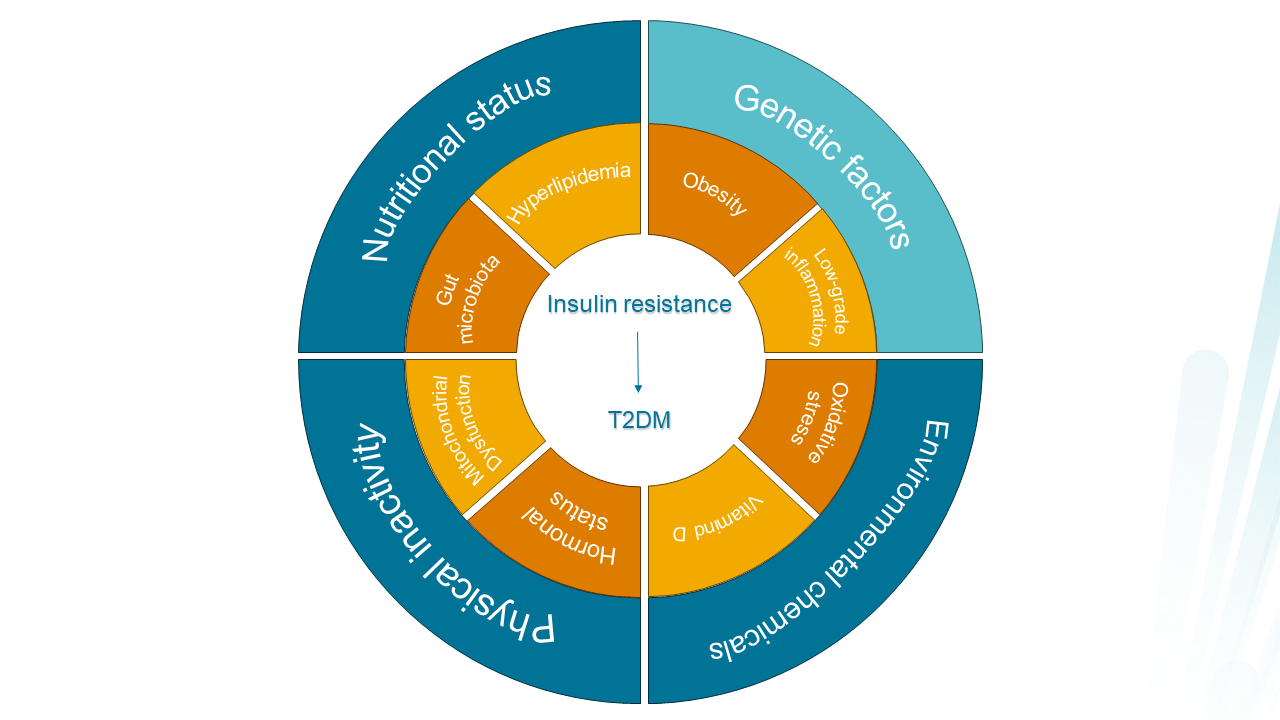
ype 2 diabetes (T2DM) is a chronic metabolic disease and is characterised by insulin resistance and insufficient insulin secretion, resulting in hyperglycaemia. The prevalence of diabetes was estimated to be 10.5% in 2021, globally. T2DM is associated with several complications, including cardiovascular complications, degradation of nerve fibres and eyesight, and impaired kidney function, especially if left untreated.
The aim is to investigate blood biomarkers related to metabolic processes (lipid, glucose, and hormone homeostasis) and their association with T2DM. Comparing pre- and post-diagnostic concentrations of blood biomarkers between T2DM cases and healthy controls will advance our knowledge of potential early predictors of T2DM and incentivise early implementations of intervention in a primary healthcare setting.
This thesis adopted a longitudinal nested case-control study based on the Tromsø Study. Participants who attended three to five surveys in the period 1986–2016 were included, where the cases were diagnosed with T2DM between the third and fourth survey. The blood biomarkers were analysed in serum samples, collected at the time of each survey. Several statistical methodologies were used to assess the associations between blood biomarkers and T2DM, and to compare how they changed over time between cases and controls and how well they could discriminate between the two groups.
Our study findings highlighted notable associations between several blood biomarkers implicated in lipid, glucose, and hormone homeostasis and the risk of developing T2DM long before the diagnosis. By utilising a combination of lipids and glycaemic biomarkers in addition to established non-invasive risk factors, it was possible to successfully identify individuals with an increased risk of developing T2DM as early as 15 years before the diagnosis. This emphasises the importance of early implementation of preventive measures to avoid or delay the onset of T2DM.
Publications and doctoral thesis:
Longitudinal changes in blood biomarkers and their ability to predict type 2 diabetes mellitus—The Tromsø study
Longitudinal changes in vitamin D concentrations and the association with type 2 diabetes mellitus: the Tromsø Study
Doctoral thesis